Documentation
¶
Documentation
¶
Overview ¶
Package jobqueue manages running and scheduling jobs.
Applications using jobqueue first create a Manager. One manager handles one or more topics. There is one processor per topic. Applications need to register topics and their processors before starting the manager.
Once started, the manager initializes the list of workers that will work on the actual jobs. At the beginning, all workers are idle.
The manager has a Store to implement persistent storage. By default, an in memory store is used. There is a MySQL-based persistent store in the "mysql" package.
New jobs are added to the manager via the Add method. The manager asks the store to create the job.
A scheduler inside manager periodically asks the Store for jobs in the Waiting state. The scheduler will tell idle workers to handle those jobs. The number of concurrent jobs can be specified via the manager option SetConcurrency.
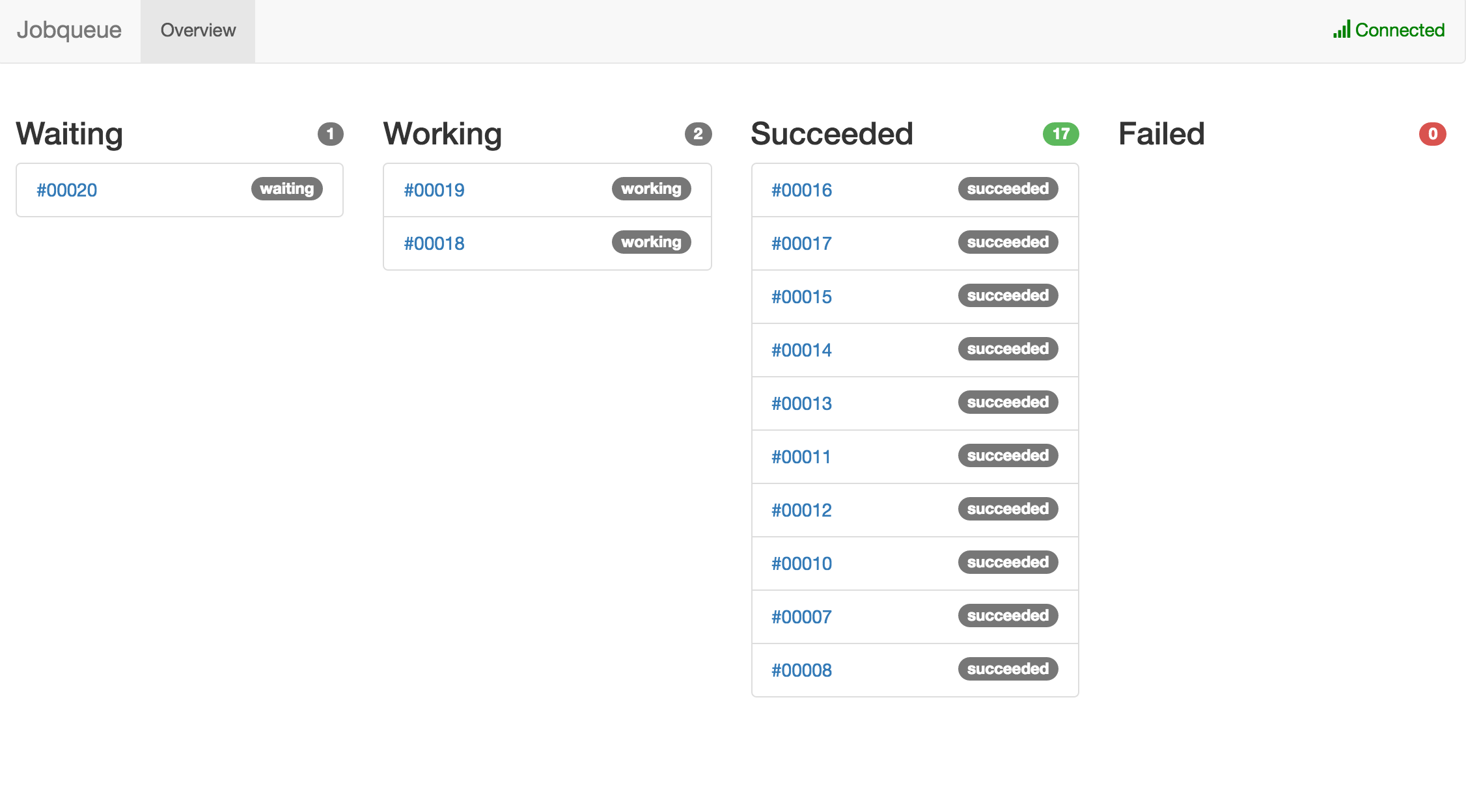
A job in jobqueue has always in one of these four states: Waiting (to be executed), Working (currently busy working on a job), Succeeded (completed successfully), and Failed (failed to complete successfully even after retrying).
A job can be configured to be retried. To do so, specify the MaxRetry field in Job. Only if the number of retries exceeds the MaxRetry value, the job gets marked as failed. Otherwise, it gets put back into Waiting state and rescheduled (after an some backoff time). The backoff function is exponential by default (see backoff.go). However, one can specify a custom backoff function by the manager option SetBackoffFunc.
If the manager crashes and gets restarted, the Store gets started via the Start method. This gives the store implementation a chance to do cleanup. E.g. the MySQL-based store implementation moves all jobs still marked as Working into the Failed state. Notice that you are responsible to prevent that two concurrent managers try to access the same database!
Index ¶
- Constants
- Variables
- type BackoffFunc
- type InMemoryStore
- func (st *InMemoryStore) Create(ctx context.Context, job *Job) error
- func (st *InMemoryStore) Delete(ctx context.Context, job *Job) error
- func (st *InMemoryStore) List(ctx context.Context, req *ListRequest) (*ListResponse, error)
- func (st *InMemoryStore) Lookup(ctx context.Context, id string) (*Job, error)
- func (st *InMemoryStore) LookupByCorrelationID(ctx context.Context, correlationID string) ([]*Job, error)
- func (st *InMemoryStore) Next() (*Job, error)
- func (st *InMemoryStore) Start(_ StartupBehaviour) error
- func (st *InMemoryStore) Stats(ctx context.Context, req *StatsRequest) (*Stats, error)
- func (st *InMemoryStore) Update(ctx context.Context, job *Job) error
- type Job
- type ListRequest
- type ListResponse
- type Logger
- type Manager
- func (m *Manager) Add(ctx context.Context, job *Job) error
- func (m *Manager) Close() error
- func (m *Manager) CloseWithTimeout(timeout time.Duration) error
- func (m *Manager) List(ctx context.Context, request *ListRequest) (*ListResponse, error)
- func (m *Manager) Lookup(ctx context.Context, id string) (*Job, error)
- func (m *Manager) LookupByCorrelationID(ctx context.Context, correlationID string) ([]*Job, error)
- func (m *Manager) Register(topic string, p Processor) error
- func (m *Manager) Start() error
- func (m *Manager) Stats(ctx context.Context, request *StatsRequest) (*Stats, error)
- func (m *Manager) Stop() error
- type ManagerOption
- type Processor
- type StartupBehaviour
- type Stats
- type StatsRequest
- type Store
Examples ¶
Constants ¶
const ( // Waiting for executing. Waiting string = "waiting" // Working is the state for currently executing jobs. Working string = "working" // Succeeded without errors. Succeeded string = "succeeded" // Failed even after retries. Failed string = "failed" )
Variables ¶
var ( // ErrNotFound must be returned from Store implementation when a certain job // could not be found in the specific data store. ErrNotFound = errors.New("jobqueue: job not found") )
Functions ¶
This section is empty.
Types ¶
type BackoffFunc ¶
BackoffFunc is a callback that returns a backoff. It is configurable via the SetBackoff option in the manager. The BackoffFunc is used to vary the timespan between retries of failed jobs.
type InMemoryStore ¶
type InMemoryStore struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
InMemoryStore is a simple in-memory store implementation. It implements the Store interface. Do not use in production.
func NewInMemoryStore ¶
func NewInMemoryStore() *InMemoryStore
NewInMemoryStore creates a new InMemoryStore.
func (*InMemoryStore) Create ¶
func (st *InMemoryStore) Create(ctx context.Context, job *Job) error
Create adds a new job.
func (*InMemoryStore) Delete ¶
func (st *InMemoryStore) Delete(ctx context.Context, job *Job) error
Delete removes the job.
func (*InMemoryStore) List ¶
func (st *InMemoryStore) List(ctx context.Context, req *ListRequest) (*ListResponse, error)
List finds matching jobs.
func (*InMemoryStore) Lookup ¶
Lookup returns the job with the specified identifier (or ErrNotFound).
func (*InMemoryStore) LookupByCorrelationID ¶
func (st *InMemoryStore) LookupByCorrelationID(ctx context.Context, correlationID string) ([]*Job, error)
LookupByCorrelationID returns the details of jobs by their correlation identifier. If no such job could be found, an empty array is returned.
func (*InMemoryStore) Next ¶
func (st *InMemoryStore) Next() (*Job, error)
Next picks the next job to execute.
func (*InMemoryStore) Start ¶
func (st *InMemoryStore) Start(_ StartupBehaviour) error
Start the store.
func (*InMemoryStore) Stats ¶
func (st *InMemoryStore) Stats(ctx context.Context, req *StatsRequest) (*Stats, error)
Stats returns statistics about the jobs in the store.
type Job ¶
type Job struct {
ID string `json:"id"` // internal identifier
Topic string `json:"topic"` // topic to find the correct processor
State string `json:"state"` // current state
Args []interface{} `json:"args"` // arguments to pass to processor
Rank int `json:"rank"` // jobs with higher ranks get executed earlier
Priority int64 `json:"prio"` // priority (highest gets executed first)
Retry int `json:"retry"` // current number of retries
MaxRetry int `json:"maxretry"` // maximum number of retries
CorrelationGroup string `json:"cgroup"` // external group
CorrelationID string `json:"cid"` // external identifier
Created int64 `json:"created"` // time when Add was called (in UnixNano)
Updated int64 `json:"updated"` // time when the job was last updated (in UnixNano)
Started int64 `json:"started"` // time when the job was started (in UnixNano)
Completed int64 `json:"completed"` // time when job reached either state Succeeded or Failed (in UnixNano)
}
Job is a task that needs to be executed.
type ListRequest ¶
type ListRequest struct {
Topic string // filter by topic
CorrelationGroup string // filter by correlation group
CorrelationID string // filter by correlation identifier
State string // filter by job state
Limit int // maximum number of jobs to return
Offset int // number of jobs to skip (for pagination)
}
ListRequest specifies a filter for listing jobs.
type ListResponse ¶
type ListResponse struct {
Total int // total number of jobs found, excluding pagination
Jobs []*Job // list of jobs
}
ListResponse is the outcome of invoking List on the Store.
type Logger ¶
type Logger interface {
Printf(format string, v ...interface{})
}
Logger defines an interface that implementers can use to redirect logging into their own application.
type Manager ¶
type Manager struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
Manager schedules job executing. Create a new manager via New.
Example ¶
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/vaibhav-sinha/jobqueue"
)
func main() {
// Create a new manager with 10 concurrent workers for rank 0 and 2 for rank 1
m := jobqueue.New(
jobqueue.SetConcurrency(0, 10),
jobqueue.SetConcurrency(1, 2),
)
// Register the processor for topic "crawl"
jobDone := make(chan struct{}, 1)
err := m.Register("crawl", func(job *jobqueue.Job) error {
url, _ := job.Args[0].(string)
fmt.Printf("Crawl %s\n", url)
jobDone <- struct{}{}
return nil
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Register failed")
return
}
// Start the manager
err = m.Start()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Start failed")
return
}
fmt.Println("Started")
// Add a new crawler job
job := &jobqueue.Job{Topic: "crawl", Args: []interface{}{"https://alt-f4.de"}}
err = m.Add(context.Background(), job)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Add failed")
return
}
fmt.Println("Job added")
// Wait for the crawler job to complete
select {
case <-jobDone:
case <-time.After(5 * time.Second):
fmt.Println("Job timed out")
return
}
// Stop/Close the manager
err = m.Stop()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Stop failed")
return
}
fmt.Println("Stopped")
}
Output: Started Job added Crawl https://alt-f4.de Stopped
func New ¶
func New(options ...ManagerOption) *Manager
New creates a new manager. Pass options to Manager to configure it.
func (*Manager) Add ¶
Add gives the manager a new job to execute. If Add returns nil, the caller can be sure the job is stored in the backing store. It will be picked up by the scheduler at a later time.
func (*Manager) Close ¶
Close is an alias to Stop. It stops the manager and waits for working jobs to finish.
func (*Manager) CloseWithTimeout ¶
CloseWithTimeout stops the manager. It waits for the specified timeout, then closes down, even if there are still jobs working. If the timeout is negative, the manager waits forever for all working jobs to end.
func (*Manager) List ¶
func (m *Manager) List(ctx context.Context, request *ListRequest) (*ListResponse, error)
List returns all jobs matching the parameters in the request.
func (*Manager) Lookup ¶
Lookup returns the job with the specified identifer. If no such job exists, ErrNotFound is returned.
func (*Manager) LookupByCorrelationID ¶
LookupByCorrelationID returns the details of jobs by their correlation identifier. If no such job could be found, an empty array is returned.
func (*Manager) Register ¶
Register registers a topic and the associated processor for jobs with that topic.
type ManagerOption ¶
type ManagerOption func(*Manager)
ManagerOption is the signature of an options provider.
func SetBackoffFunc ¶
func SetBackoffFunc(fn BackoffFunc) ManagerOption
SetBackoffFunc specifies the backoff function that returns the time span between retries of failed jobs. Exponential backoff is used by default.
func SetConcurrency ¶
func SetConcurrency(rank, n int) ManagerOption
SetConcurrency sets the maximum number of workers that will be run at the same time, for a given rank. Concurrency must be greater or equal to 1 and is 5 by default.
func SetLogger ¶
func SetLogger(logger Logger) ManagerOption
SetLogger specifies the logger to use when e.g. reporting errors.
func SetStartupBehaviour ¶
func SetStartupBehaviour(b StartupBehaviour) ManagerOption
SetStartupBehaviour specifies how an existing jobqueue will be processed during startup of a new Manager.
The None option is the default, and it won't touch the jobqueue at all.
The MarkAsFailed option will mark all running jobs as failed.
func SetStore ¶
func SetStore(store Store) ManagerOption
SetStore specifies the backing Store implementation for the manager.
type Processor ¶
Processor is responsible to process a job for a certain topic. Use job.Args to access the parameters.
type StartupBehaviour ¶
type StartupBehaviour int
StartupBehaviour specifies the behaviour of the Manager at startup.
const ( // None doesn't touch the job queue when starting up. None StartupBehaviour = iota // MarkAsFailed will mark all working jobs as failed when starting up. MarkAsFailed )
type Stats ¶
type Stats struct {
Waiting int `json:"waiting"` // number of jobs waiting to be executed
Working int `json:"working"` // number of jobs currently being executed
Succeeded int `json:"succeeded"` // number of successfully completed jobs
Failed int `json:"failed"` // number of failed jobs (even after retries)
}
Stats returns statistics about the job queue.
type StatsRequest ¶
type StatsRequest struct {
Topic string // filter by topic
CorrelationGroup string // filter by correlation group
}
StatsRequest returns information about the number of managed jobs.
type Store ¶
type Store interface {
// Start is called when the manager starts up.
// This is a good time for cleanup. E.g. a persistent store might moved
// crashed jobs from a previous run into the Failed state.
Start(StartupBehaviour) error
// Create adds a job to the store.
Create(context.Context, *Job) error
// Delete removes a job from the store.
Delete(context.Context, *Job) error
// Update updates a job in the store. This is called frequently as jobs
// are processed. Update must allow for concurrent updates, e.g. by locking.
Update(context.Context, *Job) error
// Next picks the next job to execute.
//
// The store should take the job priorities into account when picking the
// next job. Jobs with higher priorities should be executed first.
//
// If no job is ready to be executed, e.g. the job queue is idle, the
// store must return nil for both the job and the error.
Next() (*Job, error)
// Stats returns statistics about the store, e.g. the number of jobs
// waiting, working, succeeded, and failed. This is run when the manager
// starts up to get initial stats.
Stats(context.Context, *StatsRequest) (*Stats, error)
// Lookup returns the details of a job by its identifier.
// If the job could not be found, ErrNotFound must be returned.
Lookup(context.Context, string) (*Job, error)
// LookupByCorrelationID returns the details of jobs by their correlation identifier.
// If no such job could be found, an empty array is returned.
LookupByCorrelationID(context.Context, string) ([]*Job, error)
// List returns a list of jobs filtered by the ListRequest.
List(context.Context, *ListRequest) (*ListResponse, error)
}
Store implements persistent storage of jobs.