Documentation
¶
Documentation
¶
Overview ¶
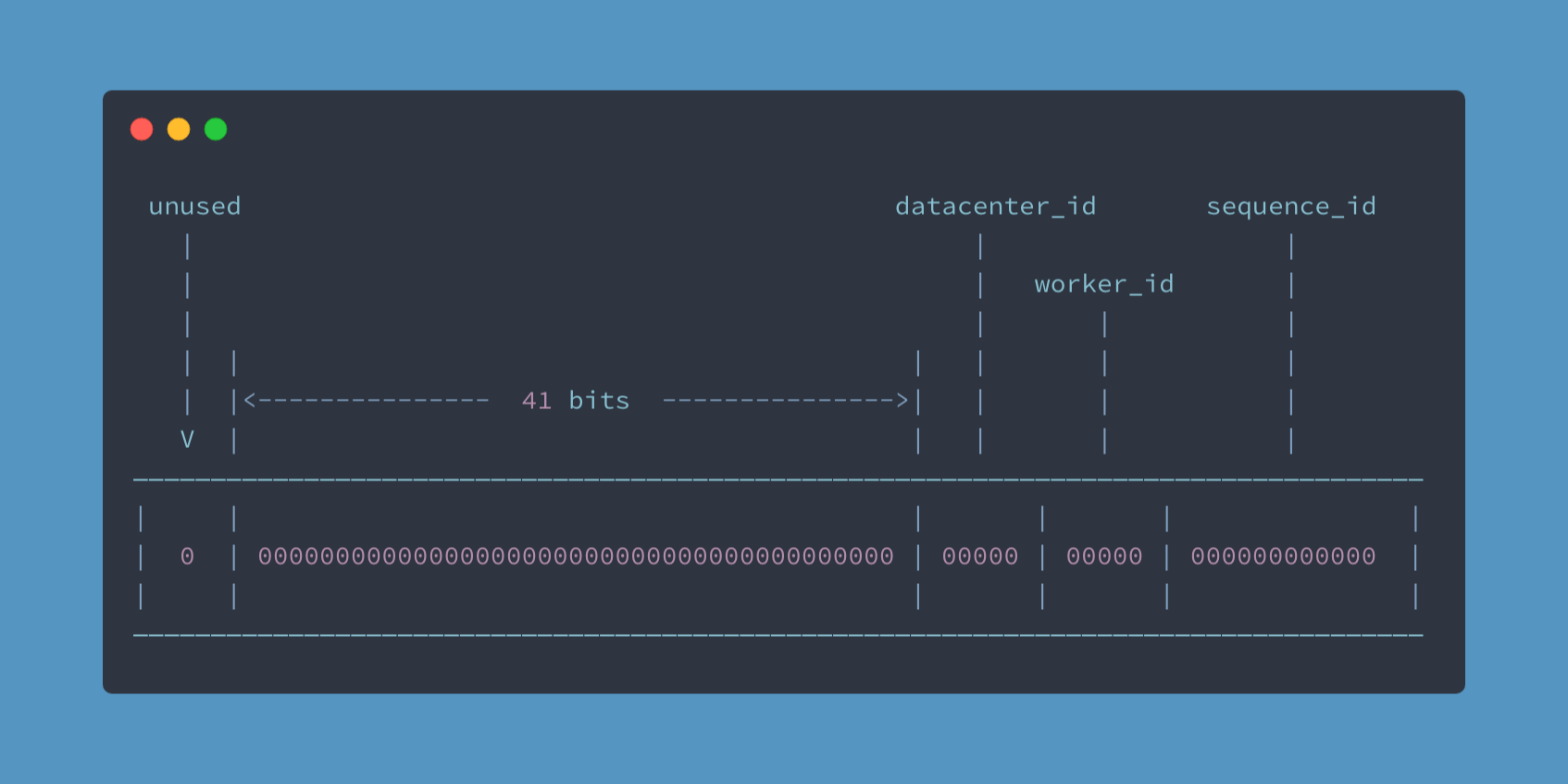
Package snowflake is a network service for generating unique ID numbers at high scale with some simple guarantees. The first bit is unused sign bit. The second part consists of a 41-bit timestamp (milliseconds) whose value is the offset of the current time relative to a certain time. The 5 bits of the third and fourth parts represent data center and worker, and max value is 2^5 -1 = 31. The last part consists of 12 bits, its means the length of the serial number generated per millisecond per working node, a maximum of 2^12 -1 = 4095 IDs can be generated in the same millisecond. In a distributed environment, five-bit datacenter and worker mean that can deploy 31 datacenters, and each datacenter can deploy up to 31 nodes. The binary length of 41 bits is at most 2^41 -1 millisecond = 69 years. So the snowflake algorithm can be used for up to 69 years, In order to maximize the use of the algorithm, you should specify a start time for it.
Index ¶
Constants ¶
const ( TimestampLength uint8 = 42 // Increased 1 bit MachineIDLength uint8 = 10 SequenceLength uint8 = 11 // Decreased 1 bit MaxSequence uint16 = 1<<SequenceLength - 1 MaxTimestamp uint64 = 1<<TimestampLength - 1 MaxMachineID uint16 = 1<<MachineIDLength - 1 )
These constants are the bit lengths of snowflake ID parts.
Variables ¶
This section is empty.
Functions ¶
func AtomicResolver ¶
AtomicResolver define as atomic sequence resolver, base on standard sync/atomic.
func ID ¶
func ID() uint64
ID use ID to generate snowflake id, and it will ignore error. if you want error info, you need use NextID method. This function is thread safe.
func NextID ¶
NextID use NextID to generate snowflake id and return an error. This function is thread safe.
func PrivateIPToMachineID ¶
func PrivateIPToMachineID() uint16
PrivateIPToMachineID convert private ip to machine id. From https://github.com/sony/sonyflake/blob/master/sonyflake.go
func SetMachineID ¶
func SetMachineID(m uint16)
SetMachineID specify the machine ID. It will panic when machined > max limit for 2^10-1. This function is thread-unsafe, recommended you call him in the main function.
func SetSequenceResolver ¶
func SetSequenceResolver(seq SequenceResolver)
SetSequenceResolver set a custom sequence resolver. This function is thread-unsafe, recommended you call him in the main function.
func SetStartTime ¶
SetStartTime set the start time for snowflake algorithm.
It will panic when:
s IsZero s > current millisecond, current millisecond - s > 2^41(69 years).
This function is thread-unsafe, recommended you call him in the main function.
Types ¶
type SID ¶
SID snowflake id
func (*SID) GenerateTime ¶
GenerateTime snowflake generate at, return a UTC time.
type SequenceResolver ¶
SequenceResolver the snowflake sequence resolver.
When you want to use the snowflake algorithm to generate unique ID, You must ensure: The sequence-number generated in the same millisecond of the same node is unique. Based on this, we create this interface provide following resolver:
AtomicResolver : base sync/atomic (by default).