tszlist
🔗 tszlist 是一种对时序数据优化的链表。




Motivation
时序数据库(TSDB)在最近几年受到了广泛的关注,而时序数据的压缩算法很大程度上决定了 TSDB 的性能。目前在业界被广泛使用的压缩算法是来自 Fackbook 的一篇论文 Gorilla: A fast, scalable, in-memory time series database,包括 Prometheus, InfluxDB, M3, TimescaleDB 在内的多种 TSDB 实现都使用了 Gorilla 中提到的 delta-of-delta 和 XOR 来分别压缩 Timestamp(int64)和 Value(float64)数据。改算法极大的压缩了存储数据点所需要的内存,收益明显。
TSDB 大多数时候都是满足监控场景的需求,这里先介绍两个概念:
- 数据点: 时序数据的数据点是一个包含 (timestamp, value) 的二元组。
- 时间线:不同 tag 的组合称为不同的时间线,比如
{"__name__": "netspeed", "host": "localhost", "iface": "eth0"}, {"__name__": "netspeed", "host": "localhost", "iface": "eth1"}。
我司内部的秒级监控系统(Neo)师承 open-falcon,不过进行了大量的重构和优化,其中的 neo-judge 组件承担着判定数据数据是否需要告警的任务,也就是说,该组件需要存储不同时间线最近 N 个数据点用来与告警规则做判定。从数据结构上来讲,这是一种有限长度的列表,超过长度限制时淘汰旧数据。 且一般来讲,判定规则只需要查询最近 n 个点(n << N)。
tszlist 是一种对以上特殊场景进行优化的数据结构,数据按 block 存储,列表冗余多一个 block, 该 block 使用 Golang 标准库 List 来存储,一旦 block 大小达到阈值(Overflow),冻结(Frozen)该 block,并使用 Gorilla 算法进行压缩,并追加至全局链表中,整体链表长度达到设置的 limit 阈值的话,删除尾部 block。
Installation
$ go get -u github.com/chenjiandongx/tszlist
所有测试代码均位于 tszlist_test.go。
Write-Operation
tszlist 写性能与标准库相差不大。
# List limit: 200000
BenchmarkTszListWrite-12 7361260 151 ns/op 102 B/op 2 allocs/op
BenchmarkStdListWrite-12 7649355 150 ns/op 102 B/op 2 allocs/op
Read-Operation
tszlist 在读取最近 n 个点时(如果 n 个点都在头部 internallist 中),略快于标准库;需要 decode block 时效率慢于标准库。
不过这个很大程度上取决于 Overflow 和 Limit 阈值的设置,不同比例的阈值会有极大的性能差异。
Round1: Tsz win
# List limit: 239, overflow: 30; search: rand.Int63(30)
# overflow 为 30,limit 为 239,所以此时落在头部 internallist 的数据点数量为 239 % 30 = 29
# 因此随机取前 30 个数据时均命中热区数据,性能较好
BenchmarkTszListRead-12 10523815 114 ns/op 235 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkStdListRead-12 4615876 270 ns/op 644 B/op 4 allocs/op
Round2: Std win
# List limit: 240, overflow: 30; search: rand.Int63(30)
# overflow 为 30,limit 为 239,所以此时落在头部 internallist 的数据点数量为 240 % 30 = 0
# 所有查询对于 tszlist 来说都要对 block 进行 decode 操作,性能较差
BenchmarkTszListRead-12 502519 2389 ns/op 2618 B/op 8 allocs/op
BenchmarkStdListRead-12 4683820 262 ns/op 644 B/op 4 allocs/op
Round3: Std win
# List limit: 240, overflow: 20; search: rand.Int63(30)
# overflow 为 30,limit 为 239,所以此时落在头部 internallist 的数据点数量为 240 % 25 = 15
BenchmarkTszListRead-12 1000000 1071 ns/op 1237 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkStdListRead-12 4389102 269 ns/op 644 B/op 4 allocs/op
Memory-Compression
tszlist 最大的优势是其内存占用要明显小于使用标准库列表实现(每条时间线 240/20 个数据点是我司的真实使用场景)。
|
时间线数量 |
每条时间线数据点 |
内存占用 |
压缩比例 |
| StdList |
20w |
240 |
3144M |
0% |
| TszList |
20w |
240(Overflow: 30) |
1127M |
64.15% |
| TszList |
20w |
240(Overflow: 25) |
1492M |
52.54% |
| StdList |
20w |
20 |
282M |
0% |
| TszList |
20w |
20(Overflow: 8) |
280M |
~0% |
| TszList |
20w |
20(Overflow: 15) |
208M |
26.24% |
Advantage
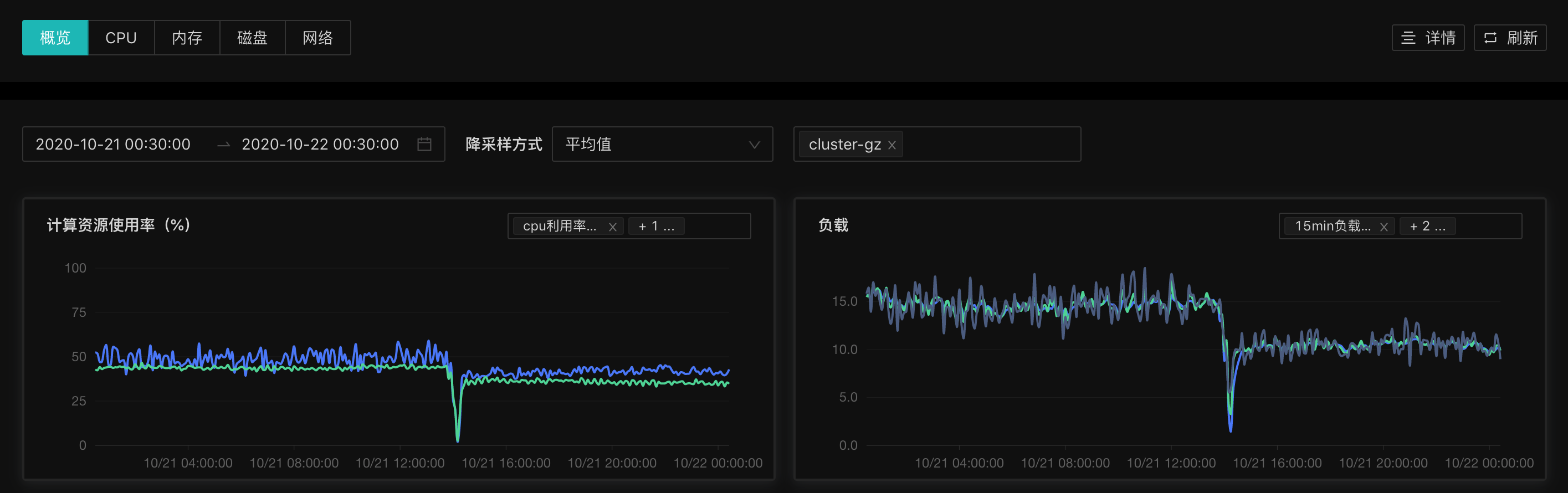
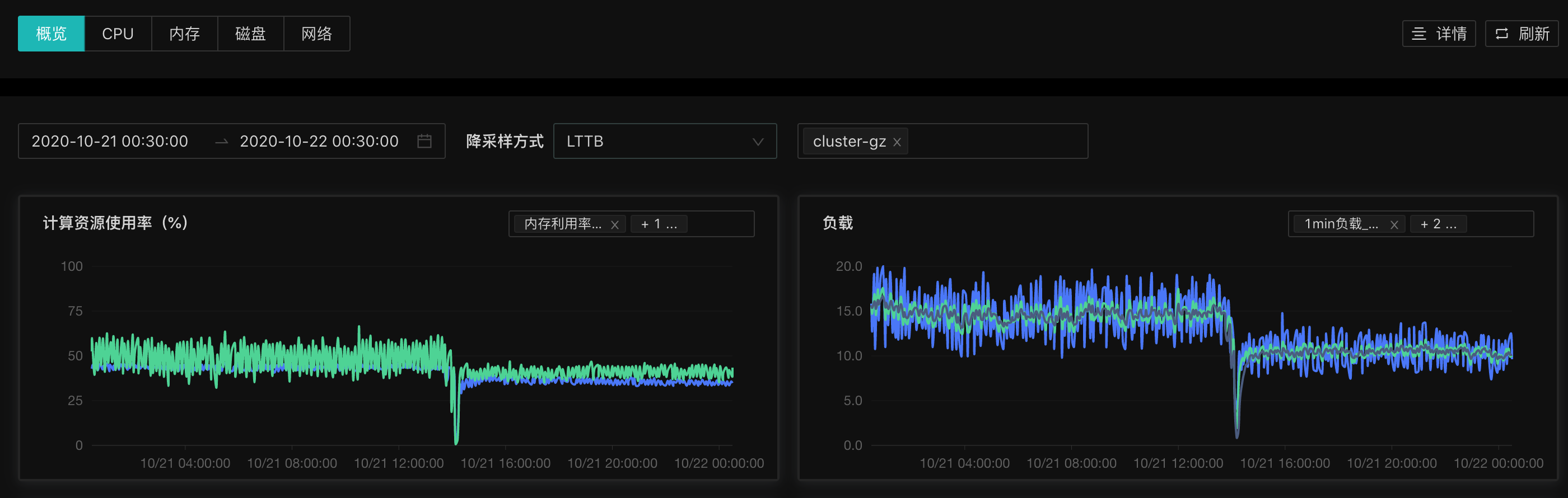
线上环境使用时,CPU 和内存使用率均出现了较为明显的下降。计算资源使用率为(内存、CPU)。
平均降采样:整体下降
LTTB 降采样:CPU 峰值波动变小
LTTB 是一种时序数据的降采样绘图方式,该算法不会对数据本身的数值进行任何修改,尽量保证绘图时波峰波谷细节。论文地址:SS_MSthesis.pdf
Usage
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/chenjiandongx/tszlist"
)
func main() {
l := tszlist.NewList(240, tszlist.WithOverflow(30))
now := time.Now().Unix()
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
l.Push(now, float64(i))
now += 5
}
fmt.Println("front5:",l.GetN(5))
fmt.Println("l.len:", l.Len())
fmt.Println("l.cap:", l.Cap())
}
// Output:
// front5: [{1603604967 9} {1603604962 8} {1603604957 7} {1603604952 6} {1603604947 5}]
// l.len: 10
// l.cap: 270
License
MIT ©chenjiandongx
 Documentation
¶
Documentation
¶


