性价比之王——宽度优先搜索
摘要
- 连通块问题
- DFS vs BFS在连通块问题上的优劣
- 劝分不劝合的编码理论
- 图的层级遍历与简单图最短路径问题
- 什么是简单图
- 复杂度最短路径有什么算法
- 最长路径用什么算法
- 什么是隐式图
- 通用的BFS模板
- 80%的人都会写错的BFS写法
- 拓扑排序
- DFS vs BFS在拓扑排序上的优劣
- 拓扑排序的四个考点
- 问有没有拓扑排序
- 求任意一个拓扑排序
- 求最小的拓扑排序
- 求拓扑排序是否唯一
BFS使用场景
-
连通块问题(Connected Component)
- 通过一个点找到图中连通的所有点
- 非递归的方式找所有方案
-
分层遍历(Level Order Traversal)
- 图的层次遍历
- 简单图最短路径(Simple Graph Shortest Path)
-
拓扑排序(Topological Sorting)
- 求任意拓扑序
- 求是否有拓扑序
- 求字典序最小的拓扑序
- 求是否唯一拓扑序
图的BFS
问最短路径
| 简单图 |
复杂图 |
| BFS |
Floyd
Dijkstra
Bellman-ford
SPFA |
- 什么是简单图
- 没有方向(undirected)
- 没有权重(unweighted)
- 两点之间最多只有一条边(no multiple edges)
- 一个点没有一条边直接连着自己(no graph loops,这里的graph loop指的是自己直接指向自己的loop)
问最长路径(不能使用BFS)
- 图可以分层:动态规划 Dynamic Programming
- 图不可以分层:深度优先搜索 DFS
分层的意思是:路径有一定方向性,不能绕圈,第i层的点只能走到第i+1层不能回到i-1层
最简洁的 BFS 算法的通用模板
// step 1: 初始化
// 把初始节点放到 queue 里,如果有多个就都放进去
// 并标记初始节点的距离为 0,记录在 distance 的 hashmap 里
// distance 有两个作用,一是判断是否已经访问过,二是记录离起点的距离
queue := []*Node{node}
distance := map[*Node]int64{
node: 0,
}
// step 2: 不断访问队列
// while 循环 + 每次 pop 队列中的一个点出来
for len(queue) > 0 {
head := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
// step 3: 拓展相邻节点
// pop 出的节点的相邻节点,加入队列并在 distance 中存储距离
for _, neighbor := range head.Neighbors {
if _, ok := distance[neighbor]; ok {
continue
}
distance[neighbor] = distance[head] + 1
queue = append(queue, neighbor)
}
}
N个点,M条边,图上BFS时间复杂度 = O(N + M),说是O(M)问题也不大,因为M一般都比N大
M最大是 O(N^2) 的级别(任意两个点之间都有边), 所以最坏情况可能是 O(N^2)
137 Clone Graph 克隆图
代码分析 —— 低耦合的清晰代码(劝分不劝和)
将整个算法分解为三个步骤:
- 找到所有点
- 复制所有点
- 复制所有边
以上三个步骤:寻点,复制点,复制边交错在一起也能跑,但可读性就差了很多
func CloneGraph(node *UndirectedGraphNode) *UndirectedGraphNode {
if node == nil {
return nil
}
nodeSet := findNodesByBfs(node)
mapping := copyNodes(nodeSet)
copyEdges(nodeSet, mapping)
return mapping[node]
}
type nodeSet map[*UndirectedGraphNode]bool
func findNodesByBfs(node *UndirectedGraphNode) nodeSet {
queue := []*UndirectedGraphNode{node}
visited := nodeSet{
node: true,
}
for len(queue) > 0 {
curNode := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
for _, neighbor := range curNode.Neighbors {
if visited[neighbor] {
continue
}
queue = append(queue, neighbor)
visited[neighbor] = true
}
}
return visited
}
func copyNodes(nodeSet nodeSet) map[*UndirectedGraphNode]*UndirectedGraphNode {
mapping := make(map[*UndirectedGraphNode]*UndirectedGraphNode)
for node := range nodeSet {
mapping[node] = &UndirectedGraphNode{
Label: node.Label,
}
}
return mapping
}
func copyEdges(nodeSet nodeSet, mapping map[*UndirectedGraphNode]*UndirectedGraphNode) {
for node := range nodeSet {
newNode := mapping[node]
for _, neighbor := range node.Neighbors {
newNeighbor := mapping[neighbor]
newNode.Neighbors = append(newNode.Neighbors, newNeighbor)
}
}
}
80% 的人都可能会写错的 BFS 算法
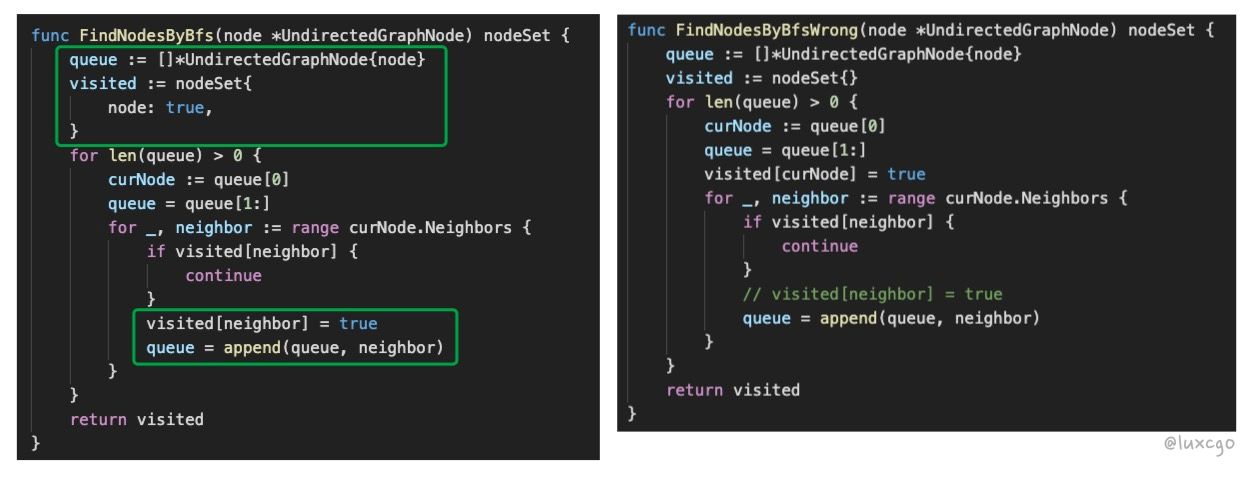
如图,左右两种写法,唯一的区别是 node 放入 visited 的时机不同
左边的是正确的,右边的是错误的,例子如下
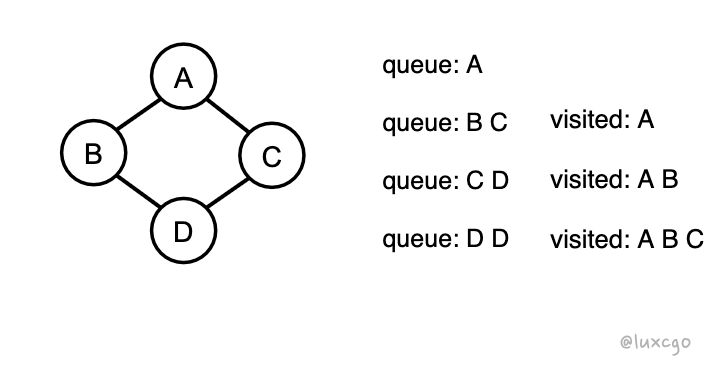
可以看到延迟放入 visited 会导致 queue 中元素重复,当节点数量更多的时候,可想而知这种重复的情况会呈指数级的增长
所以要牢记访问过一个节点后,就要立即放入已访问的集合中,这两步不能分开
BFS 分层 vs 不分层
之前都是不分层的写法,一个 node 跟着一个 node
下面提供一种分层的写法
func FindNodesByBfsWithLevel(node *UndirectedGraphNode) nodeSet {
queue := []*UndirectedGraphNode{node}
visited := nodeSet{
node: true,
}
for len(queue) > 0 {
// 每一次 range 就是一层
for range queue {
curNode := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
for _, neighbor := range curNode.Neighbors {
if visited[neighbor] {
continue
}
visited[neighbor] = true
queue = append(queue, neighbor)
}
}
}
return visited
}
120 Word Ladder 单词接龙
首先要生成指定单词的变换列表
从第一个单词开始,他的子节点就是它变换列表中的所有单词,以此类推,生成一棵树,求的就是目标节点是 end 的最短距离
getNextWords 的时间复杂度分析
两层循环 + 内部构造字符串 = O(26 * L * L) L为每个词的长度
func LadderLength(start string, end string, dict map[string]struct{}) int {
dict[end] = struct{}{}
queue := []string{start}
visited := map[string]bool{
start: true,
}
length := 1
for len(queue) > 0 {
length++
for range queue {
word := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
for _, nextWord := range getNextWords(word, dict) {
if visited[nextWord] {
continue
}
if nextWord == end {
return length
}
visited[nextWord] = true
queue = append(queue, nextWord)
}
}
}
return 0
}
func getNextWords(word string, dict map[string]struct{}) []string {
alphabet := []rune{}
for r := 'a'; r <= 'z'; r++ {
alphabet = append(alphabet, r)
}
nextWords := []string{}
for i, v := range word {
left, right := word[:i], word[i+1:]
for _, r := range alphabet {
if v == r {
continue
}
newWord := left + string(r) + right
if _, ok := dict[newWord]; ok {
nextWords = append(nextWords, newWord)
}
}
}
return nextWords
}
矩阵中的宽度优先搜索 | BFS in Matrix
433 Number of Islands
01Matrix + 联通块的个数 -> BFS/DFS
题目解析:
- 逐行逐列进行遍历
- 如果找到一个1,岛屿数量增1
- 把所有跟这个1相连的1都找出来。所有这些相连的1代表一个岛。
- 回到步骤1继续遍历
func NumIslands(grid [][]bool) int {
if len(grid) == 0 || len(grid[0]) == 0 {
return 0
}
islands := 0
visited := map[Coord]bool{}
for i, row := range grid {
for j, v := range row {
p := Coord{i, j}
if v && !visited[p] {
islands++
bfs(grid, p, visited)
}
}
}
return islands
}
func bfs(grid [][]bool, p Coord, visited map[Coord]bool) {
queue := []Coord{p}
visited[p] = true
for len(queue) > 0 {
curP := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
for _, d := range Directions {
nextP := Coord{
x: curP.x + d.x,
y: curP.y + d.y,
}
if !nextP.isValid(grid, visited) {
continue
}
queue = append(queue, nextP)
visited[nextP] = true
}
}
}
// 上下左右
var Directions = []Coord{
{-1, 0},
{1, 0},
{0, -1},
{0, 1},
}
type Coord struct {
x, y int
}
func (p Coord) isValid(grid [][]bool, visited map[Coord]bool) bool {
n, m := len(grid), len(grid[0])
if p.x < 0 || p.x >= n {
return false
}
if p.y < 0 || p.y >= m {
return false
}
if visited[p] {
return false
}
return grid[p.x][p.y]
}
611 Knight Shortest Path
使用去重的 key 是二维的坐标,也可以转换成一维的。key = X * 一列有多少元素 + Y
func ShortestPath(grid [][]bool, source *Point, destination *Point) int {
queue := []Point{*source}
cellToDisMap := map[Point]int{
*source: 0,
}
for len(queue) > 0 {
curP := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
if curP == *destination {
return cellToDisMap[curP]
}
for _, offset := range Offsets {
newP := Point{
X: curP.X + offset.X,
Y: curP.Y + offset.Y,
}
if !isValid(newP, grid, cellToDisMap) {
continue
}
queue = append(queue, newP)
cellToDisMap[newP] = cellToDisMap[curP] + 1
}
}
return -1
}
拓扑排序 | Topological Sorting
入度(In-degree):有向图(Directed Graph)中指向当前节点的点的个数(或指向当前节点的边的条数)
拓扑排序并不是传统的排序算法
一个图可能存在多个拓扑序(Topological Order),也可能不存在任何拓扑序
算法描述:
- 统计每个点的入度
- 将每个入度为 0 的点放入队列(Queue)中作为起始节点
- 不断从队列中拿出一个点,去掉这个点的所有连边(指向其他点的边),其他点的相应的入度减 1
- 一旦发现新的入度为 0 的点,丢回队列中
拓扑排序的四种不同问法
- 求任意一个拓扑排序
- 问是否存在拓扑排序
- 求是否存在且仅存在一个拓扑排序
- 求字典序最小的拓扑排序
616 Course Schedule II (问是否存在拓扑排序)
func FindOrder(numCourses int, prerequisites [][]int) []int {
// 构建图,代表(先修课->多个后修课)的映射
graph := map[int][]int{}
// 每个点的入度
inDegree := map[int]int{}
for _, v := range prerequisites {
graph[v[1]] = append(graph[v[1]], v[0])
inDegree[v[0]]++
}
queue := []int{}
for i := 0; i < numCourses; i++ {
if _, ok := inDegree[i]; !ok {
queue = append(queue, i)
}
}
numChoose := 0
topoOrder := make([]int, 0, numCourses)
for len(queue) > 0 {
nowPos := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
topoOrder = append(topoOrder, nowPos)
numChoose++
for _, v := range graph[nowPos] {
inDegree[v]--
if inDegree[v] == 0 {
queue = append(queue, v)
}
}
}
if numChoose != numCourses {
return []int{}
}
return topoOrder
}
605 Sequence Reconstruction (问拓扑排序是否唯一)
func SequenceReconstruction(org []int, seqs [][]int) bool {
graph := map[int][]int{}
inDegree := map[int]int{}
for _, seq := range seqs {
for i, node := range seq {
if i == 0 {
if _, ok := inDegree[node]; !ok {
inDegree[node] = 0
}
} else {
graph[seq[i-1]] = append(graph[seq[i-1]], node)
inDegree[node]++
}
}
}
queue := []int{}
for k, v := range inDegree {
if v == 0 {
queue = append(queue, k)
}
}
topo := []int{}
numChoose := 0
for len(queue) > 0 {
if len(queue) > 1 {
return false
}
nowPos := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
topo = append(topo, nowPos)
numChoose++
for _, v := range graph[nowPos] {
inDegree[v]--
if inDegree[v] == 0 {
queue = append(queue, v)
}
}
}
if numChoose != len(org) {
return false
}
return fmt.Sprint(org) == fmt.Sprint(topo)
}
需要处理的特殊情况 ["abc", "ab"],这种是不合法的,无论是在地球上还是在外星上
根据题目要求:一个字符串中的字母默认是同一等级的,且按照人类字典序排序。,本题中应该使用优先级队列
func AlienOrder(words []string) string {
// 初始化图
graph := map[byte][]byte{}
for _, word := range words {
for _, r := range word {
graph[byte(r)] = []byte{}
}
}
// 初始化图中的边
for i := 0; i < len(words)-1; i++ {
min := len(words[i])
if len(words[i+1]) < min {
min = len(words[i+1])
}
for j := 0; j < min; j++ {
if words[i][j] != words[i+1][j] {
graph[words[i][j]] = append(graph[words[i][j]], words[i+1][j])
break
}
if j == min-1 {
if len(words[i]) > len(words[j]) {
return ""
}
}
}
}
// 初始化入度
inDegrees := map[byte]int{}
for node := range graph {
inDegrees[node] = 0
}
for _, neighbors := range graph {
for _, neighbor := range neighbors {
inDegrees[neighbor]++
}
}
queue := &ByteHeap{}
heap.Init(queue)
for node, inDegree := range inDegrees {
if inDegree == 0 {
heap.Push(queue, node)
}
}
topoOrder := []byte{}
for queue.Len() > 0 {
curNode := heap.Pop(queue).(byte)
topoOrder = append(topoOrder, curNode)
for _, neighbor := range graph[curNode] {
inDegrees[neighbor]--
if inDegrees[neighbor] == 0 {
heap.Push(queue, neighbor)
}
}
}
if len(topoOrder) != len(graph) {
return ""
}
return string(topoOrder)
}
// A ByteHeap is a min-heap of bytes.
type ByteHeap []byte
func (h ByteHeap) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h ByteHeap) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i] < h[j] }
func (h ByteHeap) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *ByteHeap) Push(x any) {
// Push and Pop use pointer receivers because they modify the slice's length,
// not just its contents.
*h = append(*h, x.(byte))
}
func (h *ByteHeap) Pop() any {
old := *h
n := len(old)
x := old[n-1]
*h = old[0 : n-1]
return x
}
-
图上的 BFS
- 判断一个图是否是一棵树
- 搜索图中最近值为target的点
- 无向图连通块
-
矩阵上的 BFS
- 僵尸多少天吃掉所有人
- 建邮局问题 Build Post Office II
总结 | Conclusion
 Documentation
¶
Documentation
¶



